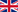
Curcumin (Diferuloylmethane) is a yellowish natural substance and the lead substance of curcuminoids. It is found naturally in high concentrations in the rhizomes (rootstocks) of Curcuma longa L. Principally native to Eastern India, it is also known as “yellowroot”, “curcuma” or “common turmeric”. It belongs to the ginger family (Zingiberaceae) and is a perennial herbaceous plant, approx. 1 metre in size. Today the plant is cultivated predominantly in India and China but also in other tropical and subtropical areas.
Curcumin (Diferuloylmethane) is a yellowish natural substance and the lead substance of curcuminoids. It is found naturally in high concentrations in the rhizomes (rootstocks) of Curcuma longa L. Principally native to Eastern India, it is also known as “yellowroot”, “curcuma” or “common turmeric”. It belongs to the ginger family (Zingiberaceae) and is a perennial herbaceous plant, approx. 1 metre in size. Today the plant is cultivated predominantly in India and China but also in other tropical and subtropical areas.
The curcuma powder extracted from the rhizomes has been used in southern and eastern Asia for more than 2000 years as a spice in food (important ingredient in curry) and a yellow dye (saffron substitute). The plant is also an integral part of ayurvedic medicine. The herbal drug was brought to Europe back in the 14th century by English and Spanish sailors. Curcumin is currently the focus of biomedical research, recognisable from a rapid increase in relevant specialised publications.
Functions of curcumin
- Curcumin is currently one of the most researched ingredients with medicinal plant origins. Findings are available in the molecular and cellular area, as well as from animal model and human clinical trials.
- The biological effects of curcumin extend to the immune system and the redox metabolism as well as the cell proliferation and biotransformation in the liver.
Useful information.
- Curcumin is practically insoluble in water, forms light non-digestible agglomerates in the gastrointestinal tract and is largely excreted unchanged in the stools. The absorption and bioavailability of curcumin from natural sources is therefore minimal.
Information on production technology
- To bypass the difficulty of the minimal bioavailability of curcumin extracts, INTERCELL Pharma uses an intelligent galenic form of curcumin in which the curcumin is covered in starch molecules. In this form, the curcumins remain in the solution in the gastrointestinal tract and an agglomeration of the curcumin is prevented. It's only in the small intestine, where the curcumin is absorbed, that the curcumin molecules are released.
- The curcumin preparation applied by INTERCELL Pharma is free of detergents and preservatives such as polysorbate, a commonly used emulsifying agent to improve the curcumin availability.
© Intercell Pharma GmbH