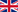
 Betaine (N,N,N,N-trimethylammonium acetate; also known as glycyl betaine) is a quaternary ammonium derivative of the amino acid glycine. Beetroot and sugar beet exhibit comparably high amounts of betaine which lend the name (lat. beta vulgaris: sugar beet) to the natural substance.
Betaine (N,N,N,N-trimethylammonium acetate; also known as glycyl betaine) is a quaternary ammonium derivative of the amino acid glycine. Beetroot and sugar beet exhibit comparably high amounts of betaine which lend the name (lat. beta vulgaris: sugar beet) to the natural substance.
Functions of betaine
- In addition to choline and S-adenosyl methionine, betaine is an important supplier of methyl groups in the metabolism and in the conversion of homocysteine into methionine. Homocysteine is a metabolic proteolysis product which accrues in the body and damages the cell structures. Betaine in this way contributes to normal metabolism of homocysteine.
Useful information.
- Betaine is the main determinant of the plasma homocysteine levels after the intake of food.
- Betaine can be formed in the body out of choline.
© Intercell Pharma GmbH