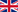
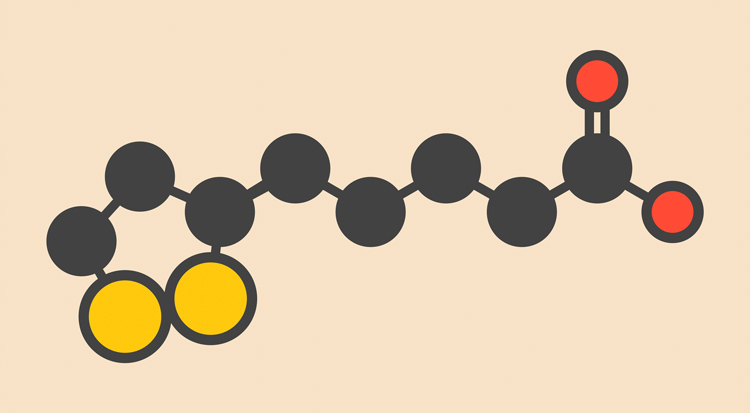
 α-Lipoic acid, also referred to as thioctic acid, is a sulphurous carboxylic acid. The valeric acid derivative is widespread in the animate natural world. Only the (R)-configured lipoic acid, also known as L-lipoic acid, is biologically active. The salts of the α-lipoic acid are lipoates. In terms of nutritional physiology, α-lipoic acid is reckoned to be one of the vitaminoids. This concerns natural substances with vitamin-like effects.
α-Lipoic acid, also referred to as thioctic acid, is a sulphurous carboxylic acid. The valeric acid derivative is widespread in the animate natural world. Only the (R)-configured lipoic acid, also known as L-lipoic acid, is biologically active. The salts of the α-lipoic acid are lipoates. In terms of nutritional physiology, α-lipoic acid is reckoned to be one of the vitaminoids. This concerns natural substances with vitamin-like effects.
Functions of α-lipoic acid
The high concentration of α-lipoic acid in tissue with a high metabolic rate and mitochondrial density, including the heart and liver, indicates the importance of the natural substance for the energy metabolism of the cells. α-lipoic acid is generated here in its reduced form, dihydrolipoic acid (6.8 dithiooctanoic acid), a biologically significant redox system. As a coenzyme, lipoic acid works closely with the vitamins B1, B2, niacin and pantothenic acid which contribute towards the normal energy metabolism of the cells.
Useful information.
- Significant quantities of α-lipoic acid are only contained in a few foods, including wheat germ and offal such as heart and liver.
Information on production technology
- INTERCELL Pharma uses a special α-lipoic acid derived without the use of solvents.
- In order to mask the typical, strong inherent smell of α-lipoic acid, in addition to a powder, pellets are available which are coated in a plant-based oil.
© Intercell Pharma GmbH