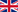
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin). Due to its presence in milk and milk products, it is also referred to as lactoflavin (from lat. lacto: consisting of milk) and belongs to the group of water-soluble vitamins. In chemical terms, it concerns a derivative of isoalloxazine with a ribityl side chain. It has a characteristically intense yellow fluorescent colouring which is was lends it its name (lat. flavus: yellow).
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin). Due to its presence in milk and milk products, it is also referred to as lactoflavin (from lat. lacto: consisting of milk) and belongs to the group of water-soluble vitamins. In chemical terms, it concerns a derivative of isoalloxazine with a ribityl side chain. It has a characteristically intense yellow fluorescent colouring which is was lends it its name (lat. flavus: yellow).
Functions of Vitamin B2
- The primary biologically active forms of vitamin B2 are flavin-mono-nucleotide (FMN) and flavin-adenine-dinucleotide (FAD). In the cell metabolism they acts as hydrogen-conveying coenzymes and contribute to a normal energy metabolism, reduction in tiredness and fatigue and the normal function of the nervous system. The vitamin also contributes to the maintenance of normal skin and mucous membranes and the red blood cells. Vitamin B2 is also a biologically active antioxidant system contributing towards protecting the cells against oxidative stress. It also supports normal vision.
Useful information.
- Vitamin B2 is very sensitive to light and oxygen and is destroyed when exposed to UV light. Losses of up to 75 % are to be expected in the storing and preparation of food.
© Intercell Pharma GmbH